Health Care Trends

Understanding Trends
Trend is a forecast of per capita claim cost increases that take into account various factors, including price inflation, utilization, government-mandated benefits, and new treatments, therapies and technology.
Although there is usually a high correlation between a trend and the actual cost increase assessed, trend and the net annual change in plan costs are not the same.
- Renewals close the gap between health care fees and actual plan costs
- A customer can experience a 5% trend and receive a 10% renewal because health care fees need to account for prospective costs that will be incurred in the future (small group claim experience is not credible and has a higher degree of volatility)
- Renewals will vary nationally based on regional pricing variations and possible changes in provider rates
- Trend increases are expected to be in the range of 9-13% for 2020, depending on the state and carrier
Other factors that impact renewals include, but are not limited to:
- High-cost claims
- High ER usage over other more cost-efficient care when applicable
- Non-adherence to medications
- Rx Specialty drug utilization
- In-network vs. out-of-network
Price Inflation Impacts
- Price inflation impacts trend and is expected to be the leading driver in 2020
- Price inflation is impacted by:
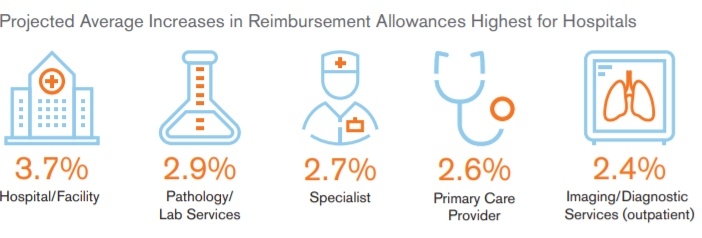
- Negotiated provider network reimbursements (Hospital trends are expected to be 2xs higher than utilization)
- New treatments, therapies and technology
- Behavioral Health or MHSA (Mental Health & Substance Abuse) is now 4% of spend
2020 General Health Care Trend Inflators
Inflator: Convenience has a cost
Increases in the availability of health care, such as retail clinics and urgent care centers, has led to higher outpatient utilization. Even if higher use of these alternative sites reduces costs, the savings will be minimized as a result of higher frequency of visits.
Inflator: Increased access for behavioral health & substance abuse (now ~4% of cost spend)
Behavioral health & substance abuse, once on the back burner of health treatments, now has the regulatory push and mainstream recognition for being a crucial part of employers’ health benefits.
Inflator: Hospital and provider network consolidations
Throughout the United States, a number of health care systems have consolidated under larger brands, and as a result, have influenced trends in the network negotiated reimbursement rates paid to providers. Reimbursement rates are projected to be higher for hospital networks than for physicians.
Inflator: Specialty drugs
2020 will see both increased prices and utilization. Specialty drugs are still trending in the double digits and now account for 24-32% of health care spend, and 35% of Rx spend. Price inflation (higher component) and increased utilization are contributing to higher costs at all ages.
2020 General Health Care Trend Deflators
Deflator: Lower Cost Settings
Employers are nudging people toward lower-cost care sites like telemedicine and urgent care facilities. Expect to see more free-standing facilities and in-home benefits like telemedicine. Providers are taking steps to move people away from hospitals and other high-cost settings.
Deflator: Care advocacy
Employers are offering employees new services that engage and guide consumers to better quality and lower-cost care.
Deflator: High performing networks like Accountable Care Organizations (ACOs) (not being utilized as initially anticipated)
Employers are exploring new benefit strategies that shift the focus from cost-sharing to leveraging high-performing networks with higher quality and lower costs such as ACOs.
Deflator: Biologics or Biosimilars
As of March 2019, 18 biosimilars have been approved in the U.S. As the market for biosimilars increases, it is expected that these options for patients will potentially decrease Rx and treatment spending. Note: Biosimilars are not generating cost savings as anticipated due to the cost to produce live organisms.